TTL Logic Levels

A majority of systems we use rely on either 3.3V or 5 V TTL Levels. TTL is an acronym for Transistor-Transistor Logic. For any logic family, there are a number of threshold voltage levels to know. Below is an example for standard 5V TTL levels:
VOH — Minimum OUTPUT Voltage level a TTL device will provide for a HIGH signal.
VIH — Minimum INPUT Voltage level to be considered a HIGH.
VOL — Maximum OUTPUT Voltage level a device will provide for a LOW signal.
VIL — Maximum INPUT Voltage level to still be considered a LOW.
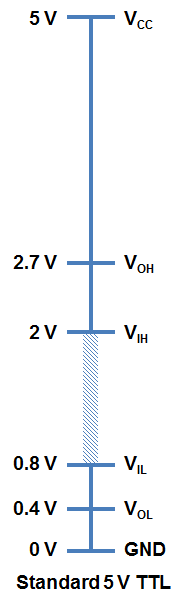
You will notice that the minimum output HIGH voltage (VOH) is 2.7 V. Basically, this means that output voltage of the device driving HIGH will always be at least 2.7 V. The minimum input HIGH voltage (VIH) is 2 V, or basically any voltage that is at least 2 V will be read in as a logic 1 (HIGH) to a TTL device.
You will also notice that there is cushion of 0.7 V between the output of one device and the input of another. This is sometimes referred to as noise margin.
Likewise, the maximum output LOW voltage (VOL) is 0.4 V. This means that a device trying to send out a logic 0 will always be below 0.4 V. The maximum input LOW voltage (VIL) is 0.8 V. So, any input signal that is below 0.8 V will still be considered a logic 0 (LOW) when read into the device.
What happens if you have a voltage that is in between 0.8 V and 2 V? Well, your guess is as good as mine. Honestly, this range of voltages is undefined and results in an invalid state, often referred to as floating. If an output pin on your device is “floating” in this range, there is no certainty with what the signal will result in. It may bounce arbitrarily between HIGH and LOW.

3.3 V CMOS Logic Levels
As technology has advanced, we have created devices that require lower power consumption and run off a lower base voltage (Vcc = 3.3 V instead of 5 V). The fabrication technique is also a bit different for 3.3 V devices that allows a smaller footprint and lower overall system costs.

In order to ensure general compatibility, you will notice that most of the voltage levels are almost all the same as 5 V devices. A 3.3 V device can interface with a 5V device without any additional components. For example, a logic 1 (HIGH) from a 3.3 V device will be at least 2.4 V. This will still be interpreted as a logic 1 (HIGH) to a 5V system because it is above the VIH of 2 V.
A word of caution, however, is when going the other direction and interfacing from a 5 V to a 3.3 V device to ensure that the 3.3 V device is 5 V tolerant. The specification you are interested in is the maximum input voltage. On certain 3.3 V devices, any voltages above 3.6 V will cause permanent damage to the chip. You can use a simple voltage divider (like a 1KΩ and a 2KΩ) to knock down 5 V signals to 3.3 V levels or use one of our logic level shifters.
thanks to sparkfun for this info.